Teldat’s Continuous Adaptive Communications Assessment Solution
Protect your IT systems and networks by adapting security on an ongoing basis, to prevent and act on threats and risks that may appear in your digital ecosystem.
Teldat’s Continuous Adaptive Risk and Trust Assessment

Today’s work environments demand the use of cybersecurity tools capable of assessing risks and threats to systems on an ongoing basis, beyond authorizing access to the network, within a zero trust CARTA framework.
- Permanent monitoring of all network elements.
- Continuous traffic analysis and machine learning to detect patterns or anomalous behavior.
- Detection of the compromised network node and notification to the SD-WAN orchestrator.
- Anticipation of threats and attacks with contextual decision making.
- Dynamic modification of the network topology to isolate threat traffic.
Market Overview – Continuous Risk and Trust Assessment

The emergence of cloud-hosted business tools and their access via the Internet is becoming a new paradigm for companies and administrations. The public cloud allows organizations cost savings (CAPEX), high processing capabilities, reliability, and scalability to meet needs.
The combination of a public cloud infrastructure and a private cloud/on-premises infrastructure gives rise to the concept of the hybrid cloud, so as to get the best of both worlds.
The move to a public cloud makes it necessary for organizations to adopt security measures in communications, detecting and preventing malware, and protecting the integrity of both their own and client data. Communications security has been around for some time. Organizations, however, do not only need the currently available IDS/IPS tools, but they also need these tools to have the ability to self-learn and prepare for new malware threats.
In addition, an organization should bear in mind that the tools and methods it uses to manage communications security may not be effective enough when taking into account newly integrated elements in the digital ecosystem, delocalized work, different access devices and, of course, constantly evolving malware and fraudulent businesses.
It is therefore essential for companies and administrations to perform regular security evaluations in the face of new threats that could compromise their IT systems.
What are the important points related to Adaptive Risk and Trust Assessment – CARTA

Continuous Threat Assessment
Network analysis tools can detect traffic patterns generated by malicious software (malware) that can cause risks to economic activity and compromise employee or customer personal data.
Automatic Learning For Threat Detection
Machine Learning techniques allow threats to be identified by learning previously labelled traffic patterns.

Identifying A Compromised Device
The system can detect a device infected with malware in order to take immediate action.

Action To Isolate Compromised Devices
Action To Isolate Compromised Devices
Prevent the spread of malware to other network elements to thus avoid compromising business activity and personal data.
Understanding CARTA Security
CARTA stands for Continuous Adaptive Risk and Trust Assessment.
In 2017, Gartner introduced the concept of adaptive security and adaptive trust assessment as a new approach to threat prevention and detection, focusing on the need for a continuous response to the ever-increasing threats and risks.
Business organizations hoping to survive in the digital sector must be able to face new challenges daily and adapt to changes constantly. One such challenge is the need to adopt new approaches emerging in the field of cybersecurity,
which can help combat the new threats and risks arising dynamically in the digital ecosystem.
Adaptive security as a prevention strategy performs continuous cybersecurity evaluations of a company’s systems, applying these evaluations to employees, customers, suppliers and partners alike. This mechanism allows companies to minimize risks by reducing their impact or the probability of compromising the existing systems.
Continuous Adaptive Risk and Trust Assessment includes implementing security architectures that adapt to their environment in order to understand behaviors and events, enabling threats to be anticipated.

Today, organizations that offer digital services allow large numbers of internal and external users to access their networks and systems. Said users access both locally and remotely and use devices/systems that are not managed by the company itself – leading to risks and threats appearing constantly.
All systems and devices should therefore be considered potentially compromised and their behaviors continuously assessed for risk and trust.
Traditional IT solutions security solutions are based on the principle of allowing or blocking access to networks and systems, analyzing the potential risk of the different users/devices.
This model, however, does not allow for sufficient contextual decision making and real-time security. It assumes that once a user or device is authorized to enter the network, it is assigned a permanent trust without reassessment. Hence, there is the possibility that these same users could later be compromised and cause a potential threat.
The model is based on a zero-trust framework, which establishes the need to continually assess all users or devices and make contextual access decisions, without granting them an intrinsic trust just because they are on the network.

The Continuous Adaptive Risk and Trust Assessment model is based on three phases:
-
- Run: This phase relies on analytics to detect anomalies in real time and machine learning. Analytics accelerates detection and automation accelerates response time, thus increasing the ability to anticipate treats and attacks. One-off authentication is not sufficient when the threat may lie beyond the door, and constant monitoring and activity tracking is essential to detect potential anomalous behavior.

-
- Build: Risk management must go beyond the domain of the company itself, i.e., it must be considered at the level of the entire ecosystem of which it is a part. This phase is based on the DevSecOps concept, whereby security is integrated from the beginning and throughout the entire software development process. For example, it is essential to detect potential security risks in the publicly available libraries used in the development of applications, eliminating these risks before incorporating them into production code.
-
- Plan: Business leaders (with the help of their security experts) must decide the level of risk that they are willing to take on in order to take advantage of the new opportunities in IT environments, such as incorporating teleworking, moving to the public cloud, or accepting new partners in the ecosystem. Continuous Adaptive cybersecurity Assessment strategic approach enables less risky decisions based on context, continually analyzing, and assessing risk and trust.

Solution & Teldat Product – CARTA
The background
Nowadays, companies and administrations develop part of their business using tools that require Internet access from customer devices. The use of the hybrid cloud is accelerating and becoming a peremptory necessity for most jobs. The Internet is becoming the best way to access public cloud services due to its good value for money.
Until recently, work environments were isolated: private data centers with access via networks such as MPLS. However, the new mixed environment (public cloud and Internet) opens the door for malware-type threats that can seriously affect company activities, causing ever-increasing financial losses year after year. While companies need a good data network at an affordable price, they also need their communications and equipment to be secure. Incorporating security tools is key here but, these tools must also be continuously updated to meet new challenges.

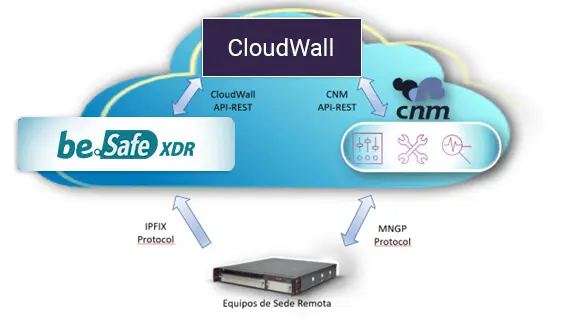
Elements that make up the Teldat CARTA solution

-
- Remote Site Devices. These are the routers that reside in the client’s facilities and constitute the communications network. The routers are designed and manufactured by Teldat S.A., which allows direct access to device software and the implementation of necessary features to achieve the project.
- be.Safe XDR. SaaS service that receives information from the Remote Site Devices, analyzes traffic for potential Zero-Day threat patterns and reports the results to the CloudWall service.
- CloudWall. SaaS service that, starting from the customer’s network topology, searches for the compromised node based on the information reported by be.Safe XDR. The information about the compromised node is reported to the Cloud Net Manager service.
- Cloud Net Manager. SaaS service responsible for orchestrating the Teldat SD-WAN solution. It receives information about the compromised node (router) in the customer’s topology and performs the necessary actions to isolate the threat traffic.
AI applied for CARTA network security and monitoring
Network monitoring tools in CARTA’s “run” phase are essential to get an overall view not only of the load on the links but also to identify which applications are being trafficked in them. In the case of the be.Safe XDR SaaS service (link to be.Safe XDR), traffic information is processed by an AI (machine Learning) layer in order to detect traffic patterns that match malware traffic already learnt by the system. The AI layer can learn about new zero-day threats, seeking to continually adapt knowledge on new risks that may affect customer networks, following Continuous Adaptive security Assessment philosophy.
be.Safe XDR is not just a monitoring tool. It also provides identification information about compromised traffic and where it originated. This information is exposed to third parties via an API Rest interface.

Isolation of compromised nodes

The information exposed by the be.Safe XDR service is used by the SaaS CloudWall service. This service selects which network links to disconnect in order to isolate compromised nodes and prevent spreading the malware infection. To do this, it needs access to information about the compromised nodes, exposed by be.Safe XDR, and the customer’s network topology, on which to act.
The topological information is provided by a network orchestrator service.
Integration with the SD-WAN solution
CloudWall’s integration with Teldat’s SDWAN orchestrator service (Cloud Net Manager) is very straightforward:
1. CloudWall accesses the SD-WAN network topology through the CNM orchestrator by means of the API Rest interface available in CNM.
2. CloudWall communicates topology changes to the CNM orchestrator to isolate the compromised nodes.
3. Since the customer’s network is SDWAN (Software Defined Network), the CNM orchestrator dynamically modifies the network topology. The modification consists of dynamically updating the configurations of the routers installed on the client.

Read our latest Blog Posts
Why the world is now looking to Europe to lead cybersecurity?
Over the past decade, cybersecurity has evolved from a specialized technical field into a core pillar of national resilience and executive responsibility. Today, boards and public administrations worldwide face a simple yet crucial question: Who can we trust to...
Increasing Cybersecurity Risks in IoT and Edge Computing in 2025
In 2025, the cybersecurity risks continues to undergo a drastic transformation due to the massive consolidation of IoT and Edge Computing. It’s not just about more connected devices — it’s about increasingly intelligent nodes with processing and decision-making...
Post-Quantum Cryptography: The Future of Digital Security
Cryptography is the backbone of modern digital security, protecting everything from banking transactions to personal communications. However, advances in quantum computing threaten to break many of today’s cryptographic systems. This has spurred the development of...