Why is segmentation needed?
Imagine a school where students don’t have different classes and all share the same space. It would be impossible to organize any sort of educational activity for them since students of different ages require different care, techniques and themes, and different subjects must be taught depending on the type of studies. Plus, if one group of students became ill, the probability of the rest becoming ill would be very high. To avoid these problems, students are divided into groups, studying different subjects taught by different teachers in different classes. This same logic is applied to software-defined networks, where each type of user has different needs, and each type of traffic must be treated separately, without affecting the rest of the network.
Segmenting the network allows us to create blocks that are llogically isolated from one another, where each segment is presented as a private network. The main advantage is that something happening in one network won’t affect other domains, enabling you to manage a potential attack or infection in a controlled way.
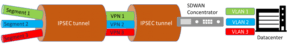
Each manufacturer employs its own particular technique to ensure segmentation. There are, however, a number of common standard elements including, for example, the use of VRFs to separate routing enviornments, the GRE protocol to generate tunnels, IPSEC encryption to encrypt information, all related to the term “VPN”. The local networks are isolated and sent by the overlay generated in the SD-WAN networks using the aforementioned techniques so that once they reach the other end they are delivered separately, usually using VLANs for each different type of traffic.
There are mulitple cases in the business world that require this type of traffic isolation, for example:
- Different audio and video traffic with different QoS requirements.
- Bank branches offering mulptle services: financial, insurance, travel, car rental, etc.
- Managing employee and guest traffic on a Wi-Fi or VOIP network.
- Computers, telephones, mobil devices and IoT in the same office.
- Users authenticated against an Active Directory or through a user/password combination.
- Laboratory environments and developing productive environments.
- Acquiring a new company with its own network address that must be included in the acquiring company’s management network.
- In retail businesses, PoS (Point-of-Sale) traffic needs to be differentiated from the internal network.
And thus we could go on to find an infinite number of cases where network segmentation greatly simplifies management, and permits the necessary traffic and policies to be maintained independently. Thanks to SD-WAN networks, these kinds of solutions, which used to take up a lot of time and effort, can now be implemented in a simple, easy to configure way.
Within Teldat, SD-WAN is a core product in which we offer the users the advantages that the SD-WAN solution has given the market, including segmentation and security.